

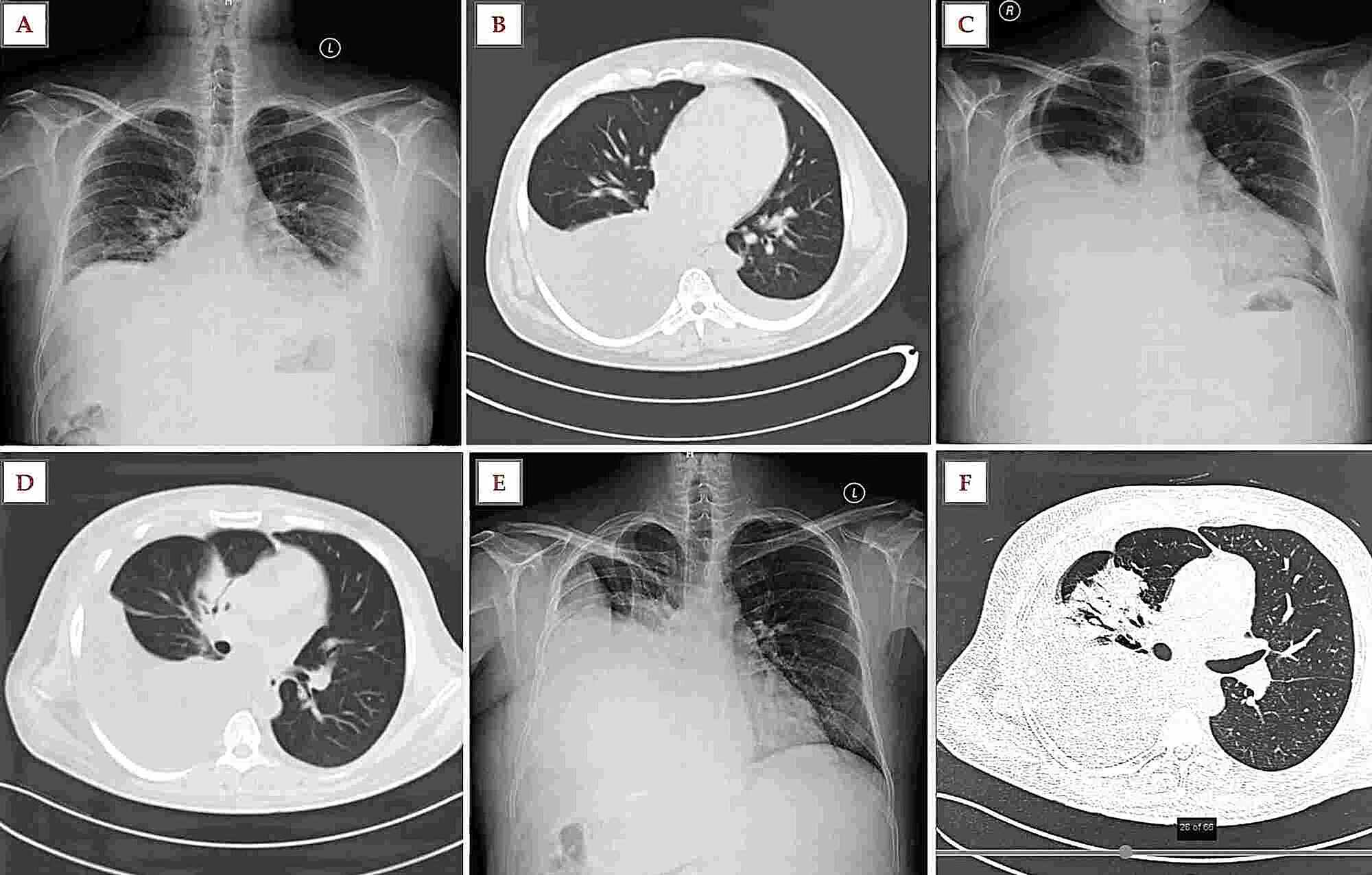
There were no differences in hospital stay (9.5☒.5 days versus 9.9☓.2 days, P = 0.68) or in mortality (2 deaths in each group, P = 0.58) between the group of patients in which antibiotic treatment was changed according to microbiological results and the group of patients in which it is not. In 48 of the 50 patients with positive microbiological results (96%), the need for pleural drainage was correctly predicted by pleural fluid parameters. Investigation of a unilateral pleural effusion in adults: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease. An initial set of tests typically includes: Fluid protein, albumin, or LD level Cell count Fluid appearance Results from these are compared to results from a blood specimen to determine whether the fluid is a transudate or an exudate. Everyone has a small amount of fluid between the lung and the chest wall (the pleural space). Microbiological studies were positive on the pleural fluid of 50 patients (19.3%). Hooper C, Lee YC, Maskell N, BTS Pleural Guideline Group. Pleural fluid testing is used to help diagnose the cause of fluid buildup in your chest cavity (pleural effusion). We evaluated the yield of microbiological studies in 259 patients with parapneumonic pleural effusion. However, this recommendation has not been tested prospectively. A small amount of fluid normally fills the pleural cavity and helps the lungs. Excess accumulation of pleural fluid or pleural effusion can occur due to an infection, disease or inflammation of the pleura, reducing the air space for the lungs to expand. Pleural effusion is buildup of fluid between the chest wall and the lung. It helps lubricate the lungs for ease respiratory movements. Congestive heart failure is the most common cause of a pleural effusion, but there is a multitude of other causes, including lung trauma or lung cancer (in which effusion is experienced in roughly half of all cases). Pleural fluid is a liquid present in the space between the chest wall and the outer lining of lungs (pleura). When this happens, breathing can be impaired, sometimes significantly. In pleural infection, it has been recommended that Gram stain and cultures should be obtained on a routine basis. Pleural effusions are encountered commonly in clinical practice because of the large number of conditions associated with pleural fluid formation. A pleural effusion is the accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
