
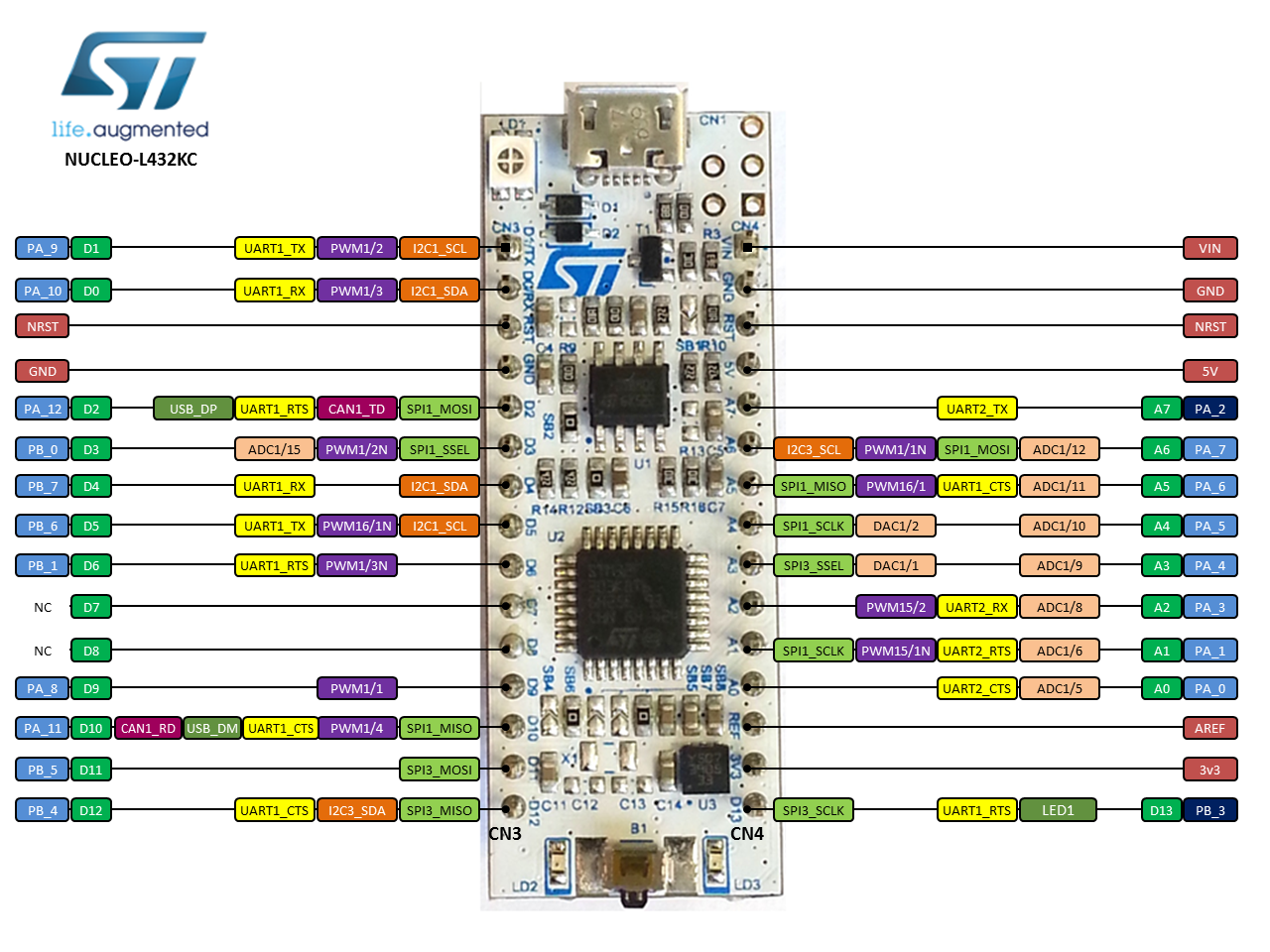
The allowable power supply voltage is from 2.7 to 5.5 volts. The Arduino LilyPad board itself is made as a circle with a diameter of 50 mm, a height of no more than 4 mm, and weighs about 8 grams. For connecting analog sensors to the board, there are six ports connected to the ADC. The Arduino LilyPad has nine general-purpose I/O ports, of which six ports can be used as PWM outputs. There are also pins on the board to connect the USB-Serial adapter, which is necessary to load sketches from the computer. The other pins are similar to the Arduino Uno pins. The “+” and “-” pins are for powering the board. There are three variants of this board: LilyPad Arduino 328 – based on the microcontroller ATmega328.Ĭonsider the LilyPad Arduino 328 board – based on the ATmega328 microcontroller. If the power supply is negative or higher than 5.5V, the board can fail. The board supply voltage is between 2.7V and 5.5V. The board is made with ATmega168V or ATmega328V microcontrollers. The printed circuit board of the LilyPad Arduino is shaped like a circle with a diameter of about 50 mm. You can wash it manually, of course, by first disconnecting the power. The electronic circuitry assembled on the fabric, including the Arduino LilyPad itself, is not afraid of washing.

The Arduino LilyPad can be sewn onto fabric and used to connect power, sensors, or actuators using conductive threads. It was designed and created by Leah Buechley together with SparkFun for use with clothing and textiles. One of the most unusual Arduino boards is the Arduino LilyPad. The Arduino platform is not represented by a single board but by a whole family of boards with different features and functionality.
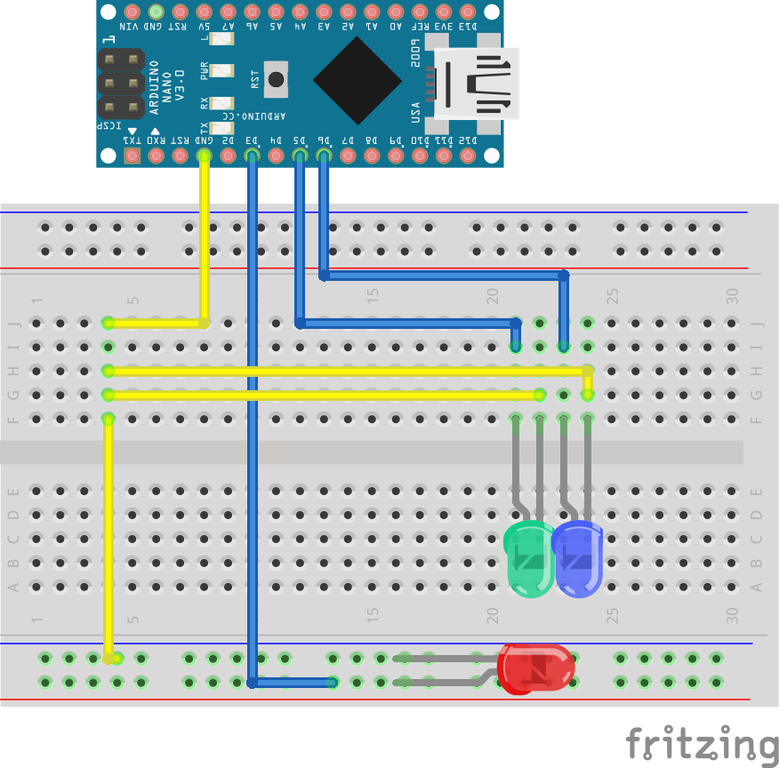
The Arduino LilyPad can be connected to a power source from a computer or other device via the micro-USB port, if available, or via the VCC port from a power supply, battery, or battery pack. This is quite handy since the board can be detached before washing. The LilyPad Simple Snap is another variation of this line, which has the pins on the circuit board as rivets. The platform can be based on the ATmega168 microcontroller or the more powerful ATmega328 microcontroller. There is a more budget version without a built-in micro-USB port, which is flashed through a programmer, like the Arduino Mini. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one on the board.The LilyPad 328P board is produced in several variants – with a built-in micro-USB port, which is used on most modern smartphones. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. There are a couple of other pins on the board: Support I2C (TWI) communication using the Wire library (documentation on the Wiring website). Additionally, some pins have specialized functionality: Analog pins 6 and 7 cannot be used as digital pins. By default they measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the analogReference() function. The Nano has 8 analog inputs, each of which provide 10 bits of resolution (i.e. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. These pins support SPI communication, which, although provided by the underlying hardware, is not currently included in the Arduino language. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function. See the attachInterrupt() function for details. These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value.
Arduino nano pinout led serial#
These pins are connected to the corresponding pins of the FTDI USB-to-TTL Serial chip. Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. In addition, some pins have specialized functions: Each pin can provide or receive a maximum of 40 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by default) of 20-50 kOhms. An Open-Source platform to create digital devices and interactive objects that sense and control physical devices.Īrduino Comparison Chart: Boards & ModulesĮach of the 14 digital pins on the Nano can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
